Loading...
Searching...
No Matches
Public Types |
Public Member Functions |
Public Attributes |
Static Public Attributes |
List of all members
rerun::archetypes::AnnotationContext Struct Reference
Archetype: The AnnotationContext provides additional information on how to display entities.
More...
#include <rerun/archetypes/annotation_context.hpp>
Public Types | |
| using | IndicatorComponent = components::IndicatorComponent< IndicatorComponentName > |
| Indicator component, used to identify the archetype when converting to a list of components. | |
Public Member Functions | |
| AnnotationContext (AnnotationContext &&other)=default | |
| AnnotationContext (rerun::components::AnnotationContext _context) | |
| size_t | num_instances () const |
| Returns the number of primary instances of this archetype. | |
Public Attributes | |
| rerun::components::AnnotationContext | context |
| List of class descriptions, mapping class indices to class names, colors etc. | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static constexpr const char | IndicatorComponentName [] |
Detailed Description
Archetype: The AnnotationContext provides additional information on how to display entities.
Entities can use ClassIds and KeypointIds to provide annotations, and the labels and colors will be looked up in the appropriate AnnotationContext. We use the first annotation context we find in the path-hierarchy when searching up through the ancestors of a given entity path.
Example
Segmentation
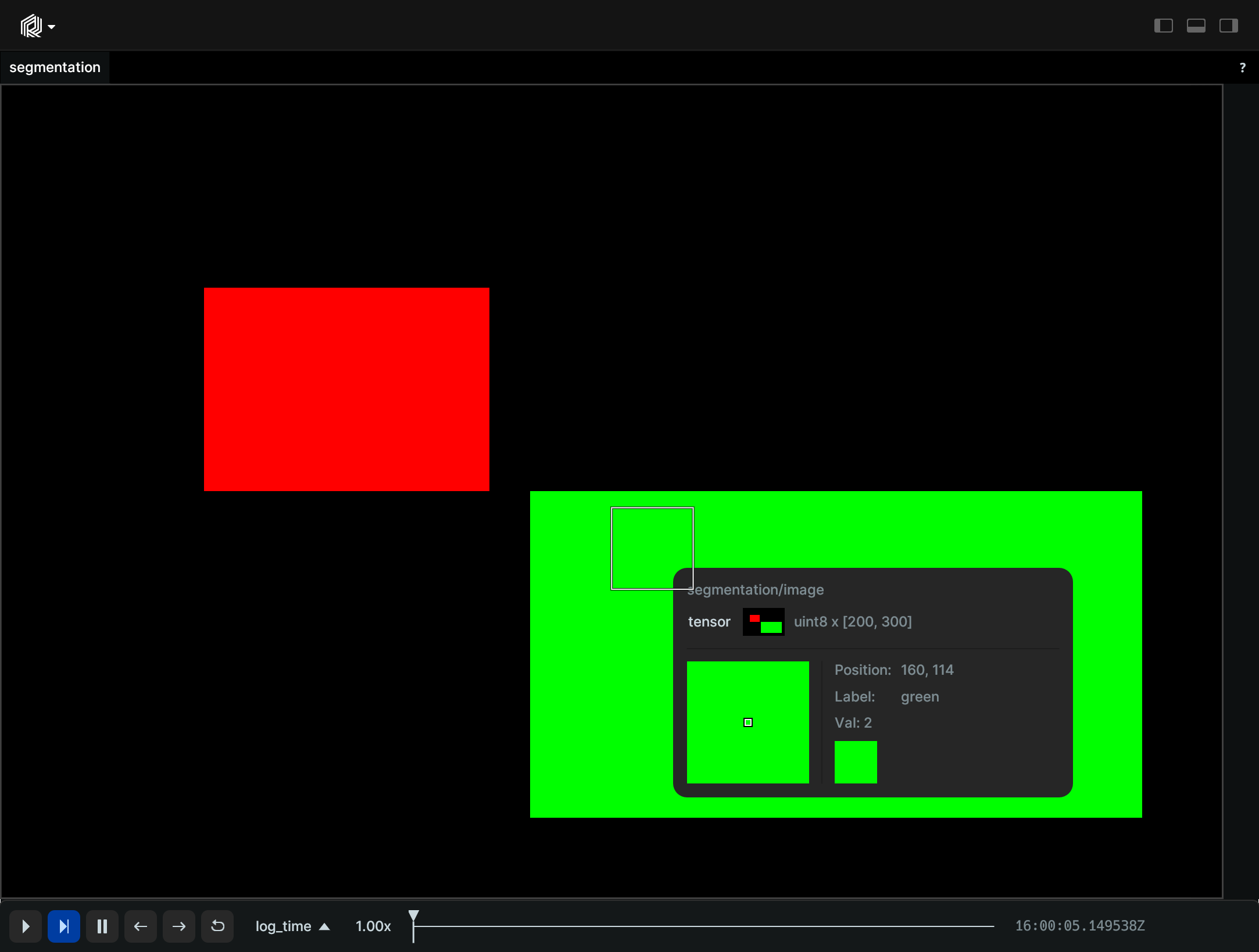
#include <rerun.hpp>
#include <algorithm> // fill_n
#include <vector>
int main() {
rec.spawn().exit_on_failure();
// create an annotation context to describe the classes
rec.log_timeless(
"segmentation",
})
);
// create a segmentation image
const int HEIGHT = 200;
const int WIDTH = 300;
std::vector<uint8_t> data(WIDTH * HEIGHT, 0);
for (auto y = 50; y <100; ++y) {
std::fill_n(data.begin() + y * WIDTH + 50, 70, static_cast<uint8_t>(1));
}
for (auto y = 100; y <180; ++y) {
std::fill_n(data.begin() + y * WIDTH + 130, 150, static_cast<uint8_t>(2));
}
rec.log("segmentation/image", rerun::SegmentationImage({HEIGHT, WIDTH}, std::move(data)));
}
A RecordingStream handles everything related to logging data into Rerun.
Definition recording_stream.hpp:57
Archetype: The AnnotationContext provides additional information on how to display entities.
Definition annotation_context.hpp:63
Archetype: An image made up of integer class-ids.
Definition segmentation_image.hpp:70
Datatype: Annotation info annotating a class id or key-point id.
Definition annotation_info.hpp:25
Datatype: An RGBA color with unmultiplied/separate alpha, in sRGB gamma space with linear alpha.
Definition rgba32.hpp:27
Member Data Documentation
◆ IndicatorComponentName
|
staticconstexpr |
Initial value:
=
"rerun.components.AnnotationContextIndicator"
The documentation for this struct was generated from the following file:
- rerun/archetypes/annotation_context.hpp