pub struct VideoFrameReference {
pub timestamp: Option<SerializedComponentBatch>,
pub video_reference: Option<SerializedComponentBatch>,
}Expand description
Archetype: References a single video frame.
Used to display individual video frames from a archetypes::AssetVideo.
To show an entire video, a video frame reference for each frame of the video should be logged.
See https://rerun.io/docs/reference/video for details of what is and isn’t supported.
§Examples
§Video with automatically determined frames
use rerun::external::anyhow;
fn main() -> anyhow::Result<()> {
let args = _args;
let Some(path) = args.get(1) else {
// TODO(#7354): Only mp4 is supported for now.
anyhow::bail!("Usage: {} <path_to_video.[mp4]>", args[0]);
};
let rec =
rerun::RecordingStreamBuilder::new("rerun_example_asset_video_auto_frames").spawn()?;
// Log video asset which is referred to by frame references.
let video_asset = rerun::AssetVideo::from_file_path(path)?;
rec.log_static("video", &video_asset)?;
// Send automatically determined video frame timestamps.
let frame_timestamps_nanos = video_asset.read_frame_timestamps_nanos()?;
let video_timestamps_nanos = frame_timestamps_nanos
.iter()
.copied()
.map(rerun::components::VideoTimestamp::from_nanos)
.collect::<Vec<_>>();
let time_column = rerun::TimeColumn::new_duration_nanos(
"video_time",
// Note timeline values don't have to be the same as the video timestamps.
frame_timestamps_nanos,
);
rec.send_columns(
"video",
[time_column],
rerun::VideoFrameReference::update_fields()
.with_many_timestamp(video_timestamps_nanos)
.columns_of_unit_batches()?,
)?;
Ok(())
}
§Demonstrates manual use of video frame references
use rerun::external::anyhow;
fn main() -> anyhow::Result<()> {
let args = _args;
let Some(path) = args.get(1) else {
// TODO(#7354): Only mp4 is supported for now.
anyhow::bail!("Usage: {} <path_to_video.[mp4]>", args[0]);
};
let rec =
rerun::RecordingStreamBuilder::new("rerun_example_asset_video_manual_frames").spawn()?;
// Log video asset which is referred to by frame references.
rec.log_static("video_asset", &rerun::AssetVideo::from_file_path(path)?)?;
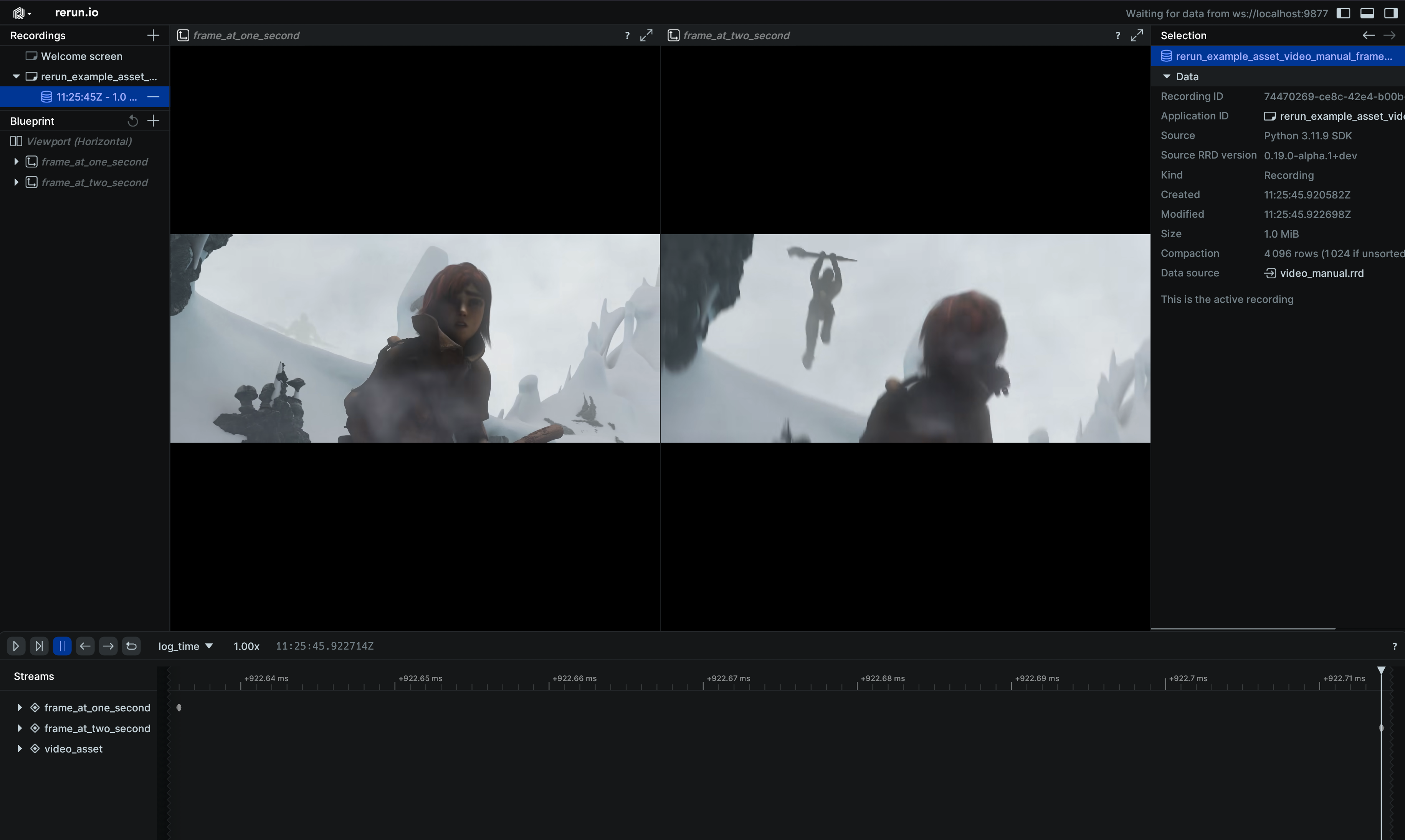
// Create two entities, showing the same video frozen at different times.
rec.log(
"frame_1s",
&rerun::VideoFrameReference::new(rerun::components::VideoTimestamp::from_secs(1.0))
.with_video_reference("video_asset"),
)?;
rec.log(
"frame_2s",
&rerun::VideoFrameReference::new(rerun::components::VideoTimestamp::from_secs(2.0))
.with_video_reference("video_asset"),
)?;
// TODO(#5520): log blueprint once supported
Ok(())
}
Fields§
§timestamp: Option<SerializedComponentBatch>References the closest video frame to this timestamp.
Note that this uses the closest video frame instead of the latest at this timestamp in order to be more forgiving of rounding errors for inprecise timestamp types.
Timestamps are relative to the start of the video, i.e. a timestamp of 0 always corresponds to the first frame. This is oftentimes equivalent to presentation timestamps (known as PTS), but in the presence of B-frames (bidirectionally predicted frames) there may be an offset on the first presentation timestamp in the video.
video_reference: Option<SerializedComponentBatch>Optional reference to an entity with a archetypes::AssetVideo.
If none is specified, the video is assumed to be at the same entity. Note that blueprint overrides on the referenced video will be ignored regardless, as this is always interpreted as a reference to the data store.
For a series of video frame references, it is recommended to specify this path only once at the beginning of the series and then rely on latest-at query semantics to keep the video reference active.
Implementations§
Source§impl VideoFrameReference
impl VideoFrameReference
Sourcepub fn descriptor_timestamp() -> ComponentDescriptor
pub fn descriptor_timestamp() -> ComponentDescriptor
Returns the ComponentDescriptor for Self::timestamp.
Sourcepub fn descriptor_video_reference() -> ComponentDescriptor
pub fn descriptor_video_reference() -> ComponentDescriptor
Returns the ComponentDescriptor for Self::video_reference.
Sourcepub fn descriptor_indicator() -> ComponentDescriptor
pub fn descriptor_indicator() -> ComponentDescriptor
Returns the ComponentDescriptor for the associated indicator component.
Source§impl VideoFrameReference
impl VideoFrameReference
Sourcepub const NUM_COMPONENTS: usize = 3usize
pub const NUM_COMPONENTS: usize = 3usize
The total number of components in the archetype: 1 required, 1 recommended, 1 optional
Source§impl VideoFrameReference
impl VideoFrameReference
Sourcepub fn new(timestamp: impl Into<VideoTimestamp>) -> VideoFrameReference
pub fn new(timestamp: impl Into<VideoTimestamp>) -> VideoFrameReference
Create a new VideoFrameReference.
Sourcepub fn update_fields() -> VideoFrameReference
pub fn update_fields() -> VideoFrameReference
Update only some specific fields of a VideoFrameReference.
Sourcepub fn clear_fields() -> VideoFrameReference
pub fn clear_fields() -> VideoFrameReference
Clear all the fields of a VideoFrameReference.
Sourcepub fn columns<I>(
self,
_lengths: I,
) -> Result<impl Iterator<Item = SerializedComponentColumn>, SerializationError>
pub fn columns<I>( self, _lengths: I, ) -> Result<impl Iterator<Item = SerializedComponentColumn>, SerializationError>
Partitions the component data into multiple sub-batches.
Specifically, this transforms the existing SerializedComponentBatches data into SerializedComponentColumns
instead, via SerializedComponentBatch::partitioned.
This makes it possible to use RecordingStream::send_columns to send columnar data directly into Rerun.
The specified lengths must sum to the total length of the component batch.
Sourcepub fn columns_of_unit_batches(
self,
) -> Result<impl Iterator<Item = SerializedComponentColumn>, SerializationError>
pub fn columns_of_unit_batches( self, ) -> Result<impl Iterator<Item = SerializedComponentColumn>, SerializationError>
Helper to partition the component data into unit-length sub-batches.
This is semantically similar to calling Self::columns with std::iter::take(1).repeat(n),
where n is automatically guessed.
Sourcepub fn with_timestamp(
self,
timestamp: impl Into<VideoTimestamp>,
) -> VideoFrameReference
pub fn with_timestamp( self, timestamp: impl Into<VideoTimestamp>, ) -> VideoFrameReference
References the closest video frame to this timestamp.
Note that this uses the closest video frame instead of the latest at this timestamp in order to be more forgiving of rounding errors for inprecise timestamp types.
Timestamps are relative to the start of the video, i.e. a timestamp of 0 always corresponds to the first frame. This is oftentimes equivalent to presentation timestamps (known as PTS), but in the presence of B-frames (bidirectionally predicted frames) there may be an offset on the first presentation timestamp in the video.
Sourcepub fn with_many_timestamp(
self,
timestamp: impl IntoIterator<Item = impl Into<VideoTimestamp>>,
) -> VideoFrameReference
pub fn with_many_timestamp( self, timestamp: impl IntoIterator<Item = impl Into<VideoTimestamp>>, ) -> VideoFrameReference
This method makes it possible to pack multiple crate::components::VideoTimestamp in a single component batch.
This only makes sense when used in conjunction with Self::columns. Self::with_timestamp should
be used when logging a single row’s worth of data.
Sourcepub fn with_video_reference(
self,
video_reference: impl Into<EntityPath>,
) -> VideoFrameReference
pub fn with_video_reference( self, video_reference: impl Into<EntityPath>, ) -> VideoFrameReference
Optional reference to an entity with a archetypes::AssetVideo.
If none is specified, the video is assumed to be at the same entity. Note that blueprint overrides on the referenced video will be ignored regardless, as this is always interpreted as a reference to the data store.
For a series of video frame references, it is recommended to specify this path only once at the beginning of the series and then rely on latest-at query semantics to keep the video reference active.
Sourcepub fn with_many_video_reference(
self,
video_reference: impl IntoIterator<Item = impl Into<EntityPath>>,
) -> VideoFrameReference
pub fn with_many_video_reference( self, video_reference: impl IntoIterator<Item = impl Into<EntityPath>>, ) -> VideoFrameReference
This method makes it possible to pack multiple crate::components::EntityPath in a single component batch.
This only makes sense when used in conjunction with Self::columns. Self::with_video_reference should
be used when logging a single row’s worth of data.
Trait Implementations§
Source§impl Archetype for VideoFrameReference
impl Archetype for VideoFrameReference
Source§type Indicator = GenericIndicatorComponent<VideoFrameReference>
type Indicator = GenericIndicatorComponent<VideoFrameReference>
Source§fn name() -> ArchetypeName
fn name() -> ArchetypeName
rerun.archetypes.Points2D.Source§fn display_name() -> &'static str
fn display_name() -> &'static str
Source§fn required_components() -> Cow<'static, [ComponentDescriptor]>
fn required_components() -> Cow<'static, [ComponentDescriptor]>
Source§fn recommended_components() -> Cow<'static, [ComponentDescriptor]>
fn recommended_components() -> Cow<'static, [ComponentDescriptor]>
Source§fn optional_components() -> Cow<'static, [ComponentDescriptor]>
fn optional_components() -> Cow<'static, [ComponentDescriptor]>
Source§fn all_components() -> Cow<'static, [ComponentDescriptor]>
fn all_components() -> Cow<'static, [ComponentDescriptor]>
Source§fn from_arrow_components(
arrow_data: impl IntoIterator<Item = (ComponentDescriptor, Arc<dyn Array>)>,
) -> Result<VideoFrameReference, DeserializationError>
fn from_arrow_components( arrow_data: impl IntoIterator<Item = (ComponentDescriptor, Arc<dyn Array>)>, ) -> Result<VideoFrameReference, DeserializationError>
ComponentNames, deserializes them
into this archetype. Read moreSource§fn from_arrow(
data: impl IntoIterator<Item = (Field, Arc<dyn Array>)>,
) -> Result<Self, DeserializationError>where
Self: Sized,
fn from_arrow(
data: impl IntoIterator<Item = (Field, Arc<dyn Array>)>,
) -> Result<Self, DeserializationError>where
Self: Sized,
Source§impl AsComponents for VideoFrameReference
impl AsComponents for VideoFrameReference
Source§fn as_serialized_batches(&self) -> Vec<SerializedComponentBatch>
fn as_serialized_batches(&self) -> Vec<SerializedComponentBatch>
SerializedComponentBatches. Read moreSource§impl Clone for VideoFrameReference
impl Clone for VideoFrameReference
Source§fn clone(&self) -> VideoFrameReference
fn clone(&self) -> VideoFrameReference
1.0.0 · Source§fn clone_from(&mut self, source: &Self)
fn clone_from(&mut self, source: &Self)
source. Read moreSource§impl Debug for VideoFrameReference
impl Debug for VideoFrameReference
Source§impl Default for VideoFrameReference
impl Default for VideoFrameReference
Source§fn default() -> VideoFrameReference
fn default() -> VideoFrameReference
Source§impl SizeBytes for VideoFrameReference
impl SizeBytes for VideoFrameReference
Source§fn heap_size_bytes(&self) -> u64
fn heap_size_bytes(&self) -> u64
self uses on the heap. Read moreSource§fn total_size_bytes(&self) -> u64
fn total_size_bytes(&self) -> u64
self in bytes, accounting for both stack and heap space.Source§fn stack_size_bytes(&self) -> u64
fn stack_size_bytes(&self) -> u64
self on the stack, in bytes. Read moreimpl ArchetypeReflectionMarker for VideoFrameReference
Auto Trait Implementations§
impl Freeze for VideoFrameReference
impl !RefUnwindSafe for VideoFrameReference
impl Send for VideoFrameReference
impl Sync for VideoFrameReference
impl Unpin for VideoFrameReference
impl !UnwindSafe for VideoFrameReference
Blanket Implementations§
Source§impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
impl<T> BorrowMut<T> for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
Source§fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
fn borrow_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T
Source§impl<T> CheckedAs for T
impl<T> CheckedAs for T
Source§fn checked_as<Dst>(self) -> Option<Dst>where
T: CheckedCast<Dst>,
fn checked_as<Dst>(self) -> Option<Dst>where
T: CheckedCast<Dst>,
Source§impl<Src, Dst> CheckedCastFrom<Src> for Dstwhere
Src: CheckedCast<Dst>,
impl<Src, Dst> CheckedCastFrom<Src> for Dstwhere
Src: CheckedCast<Dst>,
Source§fn checked_cast_from(src: Src) -> Option<Dst>
fn checked_cast_from(src: Src) -> Option<Dst>
Source§impl<T> CloneToUninit for Twhere
T: Clone,
impl<T> CloneToUninit for Twhere
T: Clone,
§impl<T> Conv for T
impl<T> Conv for T
§impl<T> Downcast for Twhere
T: Any,
impl<T> Downcast for Twhere
T: Any,
§fn into_any(self: Box<T>) -> Box<dyn Any>
fn into_any(self: Box<T>) -> Box<dyn Any>
Box<dyn Trait> (where Trait: Downcast) to Box<dyn Any>. Box<dyn Any> can
then be further downcast into Box<ConcreteType> where ConcreteType implements Trait.§fn into_any_rc(self: Rc<T>) -> Rc<dyn Any>
fn into_any_rc(self: Rc<T>) -> Rc<dyn Any>
Rc<Trait> (where Trait: Downcast) to Rc<Any>. Rc<Any> can then be
further downcast into Rc<ConcreteType> where ConcreteType implements Trait.§fn as_any(&self) -> &(dyn Any + 'static)
fn as_any(&self) -> &(dyn Any + 'static)
&Trait (where Trait: Downcast) to &Any. This is needed since Rust cannot
generate &Any’s vtable from &Trait’s.§fn as_any_mut(&mut self) -> &mut (dyn Any + 'static)
fn as_any_mut(&mut self) -> &mut (dyn Any + 'static)
&mut Trait (where Trait: Downcast) to &Any. This is needed since Rust cannot
generate &mut Any’s vtable from &mut Trait’s.§impl<T> DowncastSync for T
impl<T> DowncastSync for T
§impl<T> Instrument for T
impl<T> Instrument for T
§fn instrument(self, span: Span) -> Instrumented<Self>
fn instrument(self, span: Span) -> Instrumented<Self>
§fn in_current_span(self) -> Instrumented<Self>
fn in_current_span(self) -> Instrumented<Self>
Source§impl<T> IntoEither for T
impl<T> IntoEither for T
Source§fn into_either(self, into_left: bool) -> Either<Self, Self>
fn into_either(self, into_left: bool) -> Either<Self, Self>
self into a Left variant of Either<Self, Self>
if into_left is true.
Converts self into a Right variant of Either<Self, Self>
otherwise. Read moreSource§fn into_either_with<F>(self, into_left: F) -> Either<Self, Self>
fn into_either_with<F>(self, into_left: F) -> Either<Self, Self>
self into a Left variant of Either<Self, Self>
if into_left(&self) returns true.
Converts self into a Right variant of Either<Self, Self>
otherwise. Read moreSource§impl<T> IntoRequest<T> for T
impl<T> IntoRequest<T> for T
Source§fn into_request(self) -> Request<T>
fn into_request(self) -> Request<T>
T in a tonic::RequestSource§impl<Src, Dst> LosslessTryInto<Dst> for Srcwhere
Dst: LosslessTryFrom<Src>,
impl<Src, Dst> LosslessTryInto<Dst> for Srcwhere
Dst: LosslessTryFrom<Src>,
Source§fn lossless_try_into(self) -> Option<Dst>
fn lossless_try_into(self) -> Option<Dst>
Source§impl<Src, Dst> LossyInto<Dst> for Srcwhere
Dst: LossyFrom<Src>,
impl<Src, Dst> LossyInto<Dst> for Srcwhere
Dst: LossyFrom<Src>,
Source§fn lossy_into(self) -> Dst
fn lossy_into(self) -> Dst
§impl<T> NoneValue for Twhere
T: Default,
impl<T> NoneValue for Twhere
T: Default,
type NoneType = T
§fn null_value() -> T
fn null_value() -> T
Source§impl<T> OverflowingAs for T
impl<T> OverflowingAs for T
Source§fn overflowing_as<Dst>(self) -> (Dst, bool)where
T: OverflowingCast<Dst>,
fn overflowing_as<Dst>(self) -> (Dst, bool)where
T: OverflowingCast<Dst>,
Source§impl<Src, Dst> OverflowingCastFrom<Src> for Dstwhere
Src: OverflowingCast<Dst>,
impl<Src, Dst> OverflowingCastFrom<Src> for Dstwhere
Src: OverflowingCast<Dst>,
Source§fn overflowing_cast_from(src: Src) -> (Dst, bool)
fn overflowing_cast_from(src: Src) -> (Dst, bool)
§impl<T> Pipe for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
impl<T> Pipe for Twhere
T: ?Sized,
§fn pipe<R>(self, func: impl FnOnce(Self) -> R) -> Rwhere
Self: Sized,
fn pipe<R>(self, func: impl FnOnce(Self) -> R) -> Rwhere
Self: Sized,
§fn pipe_ref<'a, R>(&'a self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a Self) -> R) -> Rwhere
R: 'a,
fn pipe_ref<'a, R>(&'a self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a Self) -> R) -> Rwhere
R: 'a,
self and passes that borrow into the pipe function. Read more§fn pipe_ref_mut<'a, R>(&'a mut self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a mut Self) -> R) -> Rwhere
R: 'a,
fn pipe_ref_mut<'a, R>(&'a mut self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a mut Self) -> R) -> Rwhere
R: 'a,
self and passes that borrow into the pipe function. Read more§fn pipe_borrow<'a, B, R>(&'a self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a B) -> R) -> R
fn pipe_borrow<'a, B, R>(&'a self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a B) -> R) -> R
§fn pipe_borrow_mut<'a, B, R>(
&'a mut self,
func: impl FnOnce(&'a mut B) -> R,
) -> R
fn pipe_borrow_mut<'a, B, R>( &'a mut self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a mut B) -> R, ) -> R
§fn pipe_as_ref<'a, U, R>(&'a self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a U) -> R) -> R
fn pipe_as_ref<'a, U, R>(&'a self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a U) -> R) -> R
self, then passes self.as_ref() into the pipe function.§fn pipe_as_mut<'a, U, R>(&'a mut self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a mut U) -> R) -> R
fn pipe_as_mut<'a, U, R>(&'a mut self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a mut U) -> R) -> R
self, then passes self.as_mut() into the pipe
function.§fn pipe_deref<'a, T, R>(&'a self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a T) -> R) -> R
fn pipe_deref<'a, T, R>(&'a self, func: impl FnOnce(&'a T) -> R) -> R
self, then passes self.deref() into the pipe function.§impl<T> Pointable for T
impl<T> Pointable for T
Source§impl<T> SaturatingAs for T
impl<T> SaturatingAs for T
Source§fn saturating_as<Dst>(self) -> Dstwhere
T: SaturatingCast<Dst>,
fn saturating_as<Dst>(self) -> Dstwhere
T: SaturatingCast<Dst>,
Source§impl<Src, Dst> SaturatingCastFrom<Src> for Dstwhere
Src: SaturatingCast<Dst>,
impl<Src, Dst> SaturatingCastFrom<Src> for Dstwhere
Src: SaturatingCast<Dst>,
Source§fn saturating_cast_from(src: Src) -> Dst
fn saturating_cast_from(src: Src) -> Dst
§impl<T> Tap for T
impl<T> Tap for T
§fn tap_borrow<B>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&B)) -> Self
fn tap_borrow<B>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&B)) -> Self
Borrow<B> of a value. Read more§fn tap_borrow_mut<B>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut B)) -> Self
fn tap_borrow_mut<B>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut B)) -> Self
BorrowMut<B> of a value. Read more§fn tap_ref<R>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&R)) -> Self
fn tap_ref<R>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&R)) -> Self
AsRef<R> view of a value. Read more§fn tap_ref_mut<R>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut R)) -> Self
fn tap_ref_mut<R>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut R)) -> Self
AsMut<R> view of a value. Read more§fn tap_deref<T>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&T)) -> Self
fn tap_deref<T>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&T)) -> Self
Deref::Target of a value. Read more§fn tap_deref_mut<T>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut T)) -> Self
fn tap_deref_mut<T>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut T)) -> Self
Deref::Target of a value. Read more§fn tap_dbg(self, func: impl FnOnce(&Self)) -> Self
fn tap_dbg(self, func: impl FnOnce(&Self)) -> Self
.tap() only in debug builds, and is erased in release builds.§fn tap_mut_dbg(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut Self)) -> Self
fn tap_mut_dbg(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut Self)) -> Self
.tap_mut() only in debug builds, and is erased in release
builds.§fn tap_borrow_dbg<B>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&B)) -> Self
fn tap_borrow_dbg<B>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&B)) -> Self
.tap_borrow() only in debug builds, and is erased in release
builds.§fn tap_borrow_mut_dbg<B>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut B)) -> Self
fn tap_borrow_mut_dbg<B>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut B)) -> Self
.tap_borrow_mut() only in debug builds, and is erased in release
builds.§fn tap_ref_dbg<R>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&R)) -> Self
fn tap_ref_dbg<R>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&R)) -> Self
.tap_ref() only in debug builds, and is erased in release
builds.§fn tap_ref_mut_dbg<R>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut R)) -> Self
fn tap_ref_mut_dbg<R>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&mut R)) -> Self
.tap_ref_mut() only in debug builds, and is erased in release
builds.§fn tap_deref_dbg<T>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&T)) -> Self
fn tap_deref_dbg<T>(self, func: impl FnOnce(&T)) -> Self
.tap_deref() only in debug builds, and is erased in release
builds.